
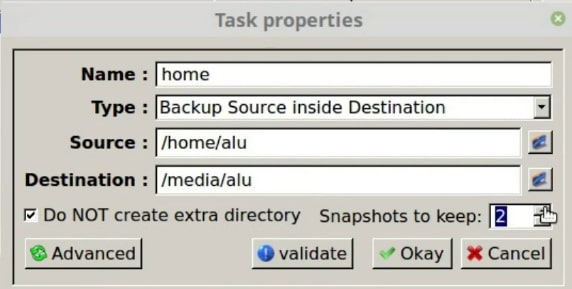
delete Delete files that don't exist on the sending side
#Grsync ignore folder update
existing Only update files that already exist C, -cvs-exclude Auto ignore files in the same way CVS does c, -checksum Skip based on checksum, not mod-time & size z, -compress Compress file data during the transfer backup-dir=DIR Make backups into this directory b, -backup Make backups (see -suffix & -backup-dir)
#Grsync ignore folder archive
W, -whole-file Copy whole files, no incremental checksĭestination options: -a, -archive Archive mode equals -rlptgoD (no -H,-A,-X) timeout=SECONDS Set IO timeout in seconds numeric-ids Don't map uid/gid values by user/group name rsync-path=PATH Specify path to rsync on the remote machine B, -block-size=SIZE Force a fixed checksum block-size (default 700) x, -one-file-system Don't cross filesystem boundaries S, -sparse Handle sparse files efficiently remove-source-files Sender removes synchronized files (non-dir) o, -owner Preserve owner (super-user only) D, -devices -specials Preserve devices (super-user only) +files devices Preserve device files (super-user only) munge-links Munge symlinks to make them safer safe-links Ignore links outside the destination tree copy-unsafe-links Only "unsafe" symlinks are transformed L, -copy-links Transform symlink into referent file/dir
#Grsync ignore folder how to
How to copy: -n, -dry-run Perform a trial run with no changes made
include-from=FILE Read include patterns from FILE include=PATTERN Don't exclude files matching PATTERN modify-window=NUM Timestamp window (seconds) for file match (default=0) size-only Only use file size when determining if a file should be transferred I, -ignore-times Don't exclude files that match length and time exclude-from=FILE Read exclude patterns from FILE exclude=PATTERN Exclude files matching PATTERN What to copy: -r, -recursive Recurse into directories Here are the commonly used options for rsync, straight from the manual:


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
